We all want to have abundant, shiny, easy to brush…. hair. There are some with luck but others, due to external causes or genetic heritage, have to fight to maintain their hair under control and healthy everyday.
This is the first post of a series related to hair: physiology, pathologies, ingredients to avoid, how to apply hair care products, advice, massages… The goal is to enhance knowledge and clear doubts about hair. So, let’s go.
The main function of hair is to protect us from the sun. It removes more than 99% of the sun’s radiation and it transforms that attack into heat. This is a very effective way to avoid DNA damage that could develop pathologies or important illnesses.
*** By the way, if one is going to be under the sun for a while or under extreme weather, it is very important and very recommended to wear a hat or cap.
General hair structure
Hair is born into a follicle. That follicle develops before birth, from the 9th week until the 22nd.
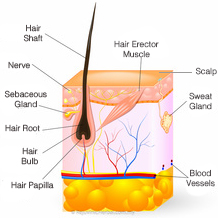
– Hair follicle: where hair grows.
– Sebaceous gland: it secretes fat to the hair follicle under the scalp.
– Hair erector muscle: It is only active if it is cold or one is in danger or is afraid of something. In that moment, it contracts and goosebumps appear.
Hair anatomy is also composed of blood vessels, a sweat gland, nerves that give the local sensitivity and: hair bulb, hair or dermal papilla, hair root, hair shaft
Hair shaft structure
1- Medulla: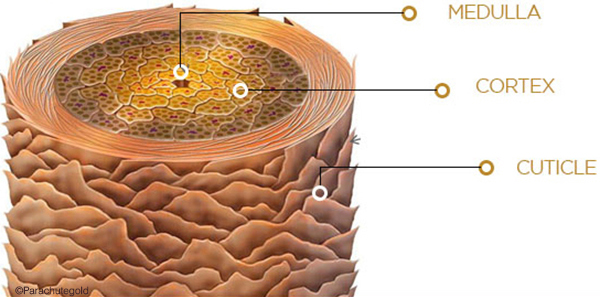
It is the centre of the hair and it is formed by keratin cells and fat from the sebaceous gland. Sometimes a hair shaft can have 2 medullas inside or none. Depending on this, hair is thicker or thinner, stronger or weaker.
2- Cortex:
It occupies close to 90% of a hair shaft. It is in charge of the shape and elasticity hair. Rind contains melanin that can be seen through the cuticle, which is transparent, and it gives the hair its natural colour.
3- Cuticle:
It is the external part of the hair. It is formed by flat cells and they are placed like fish scales, which consists of around 5 or 10 layers. They give resilience to hair. Its function is to regulate the absorption of hydration.
The cuticle is transparent and protects the rest of hair structure from external aggressions. For example, it protects from shampooing, dyeing, brushing, drying and other extreme treatments. It also protects hair from the external environment and weather.
It is very important to maintain hair at an optimal level of hydration because in this way, keratin and fibres are unified and they give enough strength and elasticity to have healthy hair. Without hydration, hair becomes thin and breaks easily.
Hair growth cycle
In general, it is not known that the cycle of hair growth is divided into four phases, which starts in the follicle:
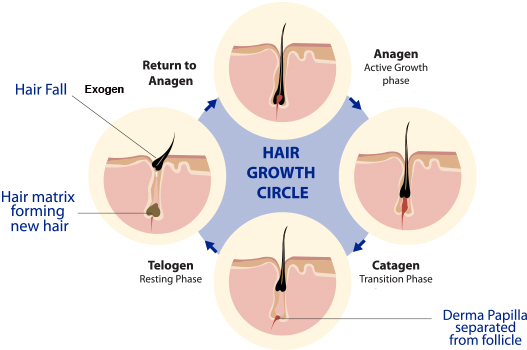 1- Anagen: grow
1- Anagen: grow
80% or 90% of hair is in this phase, which lasts approximately 3 years. In this phase, the hair grows all the time.
2- Catagen: transition
It is a short transition phase between the anagen and telogen. During this time, the growing stops and lasts for 3 to 4 weeks. 5% of hair is in this phase. The hair follicle shrinks and detaches from the dermica papilla (the deepest part inside the scalp).
3- Telogen: rest
This is a quiet phase that last 3 or 4 months. Around 10% or 15% of hair is in this phase. Whilst old hair is resting, a new one grows in the same place.
4- Exogen: go away
The follicle falls down and the new cycle starts. Approximately between 35 to 100 or 150 hairs fall out daily. That is the normal shedding.
Do you know that there are a total of 25 or 30 cycles throughout life? However, this growth cycle can be interrupted because of the masculine hormones or other factors like stress or medicines. After these cycles or an interruption of the growth cycle, alopecia appears: no more follicles are growing anymore.
In few days, I will let you know 10 curiosities about hair! You do not even imagine them! 😀
See you!


